Abstract
Introduction: Daratumumab is a human IgGκ monoclonal antibody targeting CD38 with a direct on-tumor and immunomodulatory mechanism of action. In the global phase 3 ALCYONE trial, the addition of daratumumab to bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone (D-VMP) resulted in improved outcomes over bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone (VMP) alone in transplant-ineligible patients (pts) with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM). At a median follow-up of 16.5 months, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was not reached (NR) for the D-VMP group versus 18.1 months for the VMP group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.50; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.38-0.65; P<0.001). With extended follow-up (median follow-up, 40.1 months), D-VMP demonstrated a significant overall survival benefit (HR, 0.60; 95% CI, 0.46-0.80; P=0.0003) and continued to demonstrate significant improvement in PFS versus VMP with no new safety concerns. In the phase 3 OCTANS trial, at a median follow-up of 12.3 months, D-VMP significantly prolonged PFS versus VMP in transplant-ineligible Asian pts with NDMM (median PFS, NR vs 18.2 months; HR, 0.43; 95% CI, 0.24-0.77; P=0.0033). Here, we present a pooled analysis of transplant-ineligible NDMM pts from OCTANS and ALYCONE.
Methods: Eligible pts in OCTANS and ALCYONE were ≥18 years of age, had NDMM, and were not eligible for autologous stem cell transplant due to age (≥65 years) or comorbidities. All pts received up to 9 (42-day) cycles of bortezomib 1.3 mg/m 2 subcutaneously twice weekly on Weeks 1, 2, 4, and 5 of Cycle 1 and once weekly on Weeks 1, 2, 4, and 5 of Cycles 2-9; melphalan 9 mg/m 2 orally once daily on Days 1-4 of each cycle; and prednisone 60 mg/m 2 orally once daily on Days 1-4 of each cycle. For pts in the D-VMP group, daratumumab 16 mg/kg intravenously was administered once weekly in Cycle 1, once every 3 weeks in Cycles 2-9, and once every 4 weeks thereafter until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Cytogenetic risk was determined at baseline via local fluorescence in situ hybridization or karyotype analysis; pts with high cytogenetic risk had a del17p, t(4;14), or t(14;16) abnormality.
Results: In total, 220 Asian pts were randomized (D-VMP, n=146; VMP, n=74) in the OCTANS study and 706 global pts were randomized (D-VMP, n=350; VMP, n=356) in the ALCYONE study. The median age was 69 (range, 57-84) years in OCTANS and 71 (range 40-93) years in ALCYONE. Among pts with available cytogenetic results, 48/219 (21.9%) pts in OCTANS and 98/616 (15.9%) pts in ALCYONE had high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities.
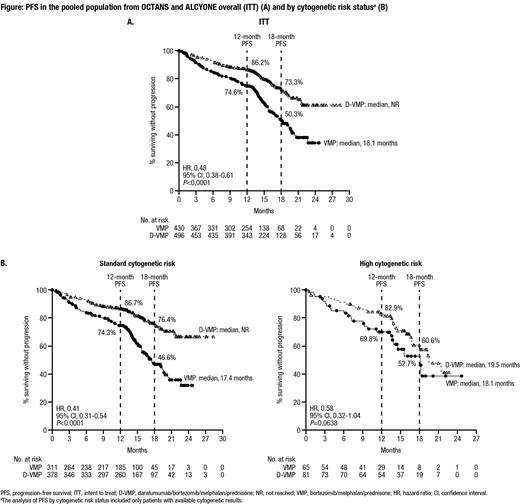
At a median follow-up of 12.3 months in OCTANS and 16.5 months in ALCYONE, in the pooled intent-to-treat (ITT) population from OCTANS and ALCYONE, the estimated 12-month PFS rate was 86.2% in the D-VMP group (n=496) versus 74.6% in the VMP group (n=430), and the estimated 18-month PFS rate was 73.3% versus 50.3%, respectively; the median PFS was NR in the D-VMP group versus 18.1 months in the VMP group (HR, 0.48; 95% CI, 0.38-0.61; P<0.0001) (Figure A). In the pooled subgroup of pts with standard cytogenetic risk, the estimated 12-month PFS was 86.7% in the D-VMP group (n=378) versus 74.3% in the VMP group (n=311), and the estimated 18-month PFS rate was 76.4% versus 46.6%, respectively; the median PFS was NR in the D-VMP group versus 17.4 months in the VMP group (HR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.31-0.54; P<0.0001) (Figure B). In the pooled subgroup of pts with high cytogenetic risk, the estimated 12-month PFS rate was 82.9% in the D-VMP group (n=81) versus 69.8% in the VMP group (n=65), and the estimated 18-month PFS rate was 60.6% versus 52.7%, respectively; the median PFS was 19.5 months in the D-VMP group versus 18.1 months in the VMP group (HR, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.32-1.04; P=0.0638) (Figure B). Analysis of the pooled ITT population showed PFS and overall response rate (ORR) benefits with D-VMP across clinically relevant subgroups, including pts aged ≥75 years, pts with impaired renal function (creatine clearance ≤60 mL/min), and pts with International Staging System Stage III disease.
Conclusion: In a pooled analysis of Asian pts from OCTANS and global pts from ALCYONE, D-VMP demonstrated clinical benefit versus VMP in transplant-ineligible pts with NDMM. The benefit of D-VMP versus VMP was observed across clinically relevant subgroups. These results support the use of D-VMP in transplant-ineligible pts with NDMM.
Kim: BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Li: Suzhou Zelgen Biopharmaceuticals Co.,Ltd.: Honoraria. Chim: Janssen, Takeda & Amgen: Other: received sponsorship for overseas meetings. Rodriguez-Otero: Clínica Universidad de Navarra: Current Employment; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene-BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GSK: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Consultancy; Sanofi: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kite: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Honoraria; Regeneron: Honoraria. Dimopoulos: Takeda: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Beigene: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria. Wroblewski: Janssen: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Carson: Janssen: Current Employment. Qi: Janssen: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Wang: Janssen: Current Employment. Song: Janssen: Current Employment. Jia: Janssen: Current Employment. Yang: Janssen: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Liu: Janssen: Ended employment in the past 24 months. Li: Janssen: Current Employment. Zhang: Janssen: Current Employment. Wang: AbbVie: Consultancy; Astellas Pharma, Inc.: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal